Our History
Origins of the World Federalist Movement
Organized Canadian world federalist groups emerged after the Second World War, paralleling similar movements across the globe. The devastating impact of the war, the revelation of the Holocaust horrors, and the ominous threat of atomic warfare underscored the need for a transformative approach to global governance. The Second World War left Europe devastated, the horror of the Holocaust was revealed, and atomic war, first used on the civilian populations of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, threatened all of humanity. The world federalists understood the structural constraints of the United Nations Organization and the urgent need to develop democratic world institutions that could make and enforce world law.
World Federalist Movement - Canada
In 1951, five independent world federalist groups in Montreal, Ottawa, Toronto, Winnipeg and Saskatoon came together to endorse a national constitution and form the World Federalists of Canada. Formal Government of Canada letters patent were obtained in 1965. A sister organization, a CRA registered charitable organization, the World Federalist Foundation was established in 1986. In spite of the frustrations of the Cold War, the World Federalists of Canada (now called World Federalist Movement – Canada) continued to champion step-by-step improvements in the way human society governs itself on a global scale.
Building a Global Community
Today, two decades after the end of the Cold War, the value of democratically accountable global governance has never been clearer. Our personal lives have become integrated with the life of an emerging world community, and global trends, conditions and patterns tie us to each other and the Earth. Individual citizens have a stake in the outcome of world affairs and ought to have democratic rights over decisions affecting the world community.
Timeline
Below is a brief timeline featuring significant dates that have shaped the trajectory of the World Federalist Movement Canada (WFM-C) and the broader World Federalist Movement. This chronological overview highlights key milestones, accomplishments, and pivotal moments that have contributed to our ongoing mission of advocating for improved global governance for a more harmonious world.

1919 - Establishing the League of Nations
The League of Nations is established after World War I with the aim of promoting international cooperation and preventing future conflicts. While it falls short of a true world government, it is a step towards international governance.
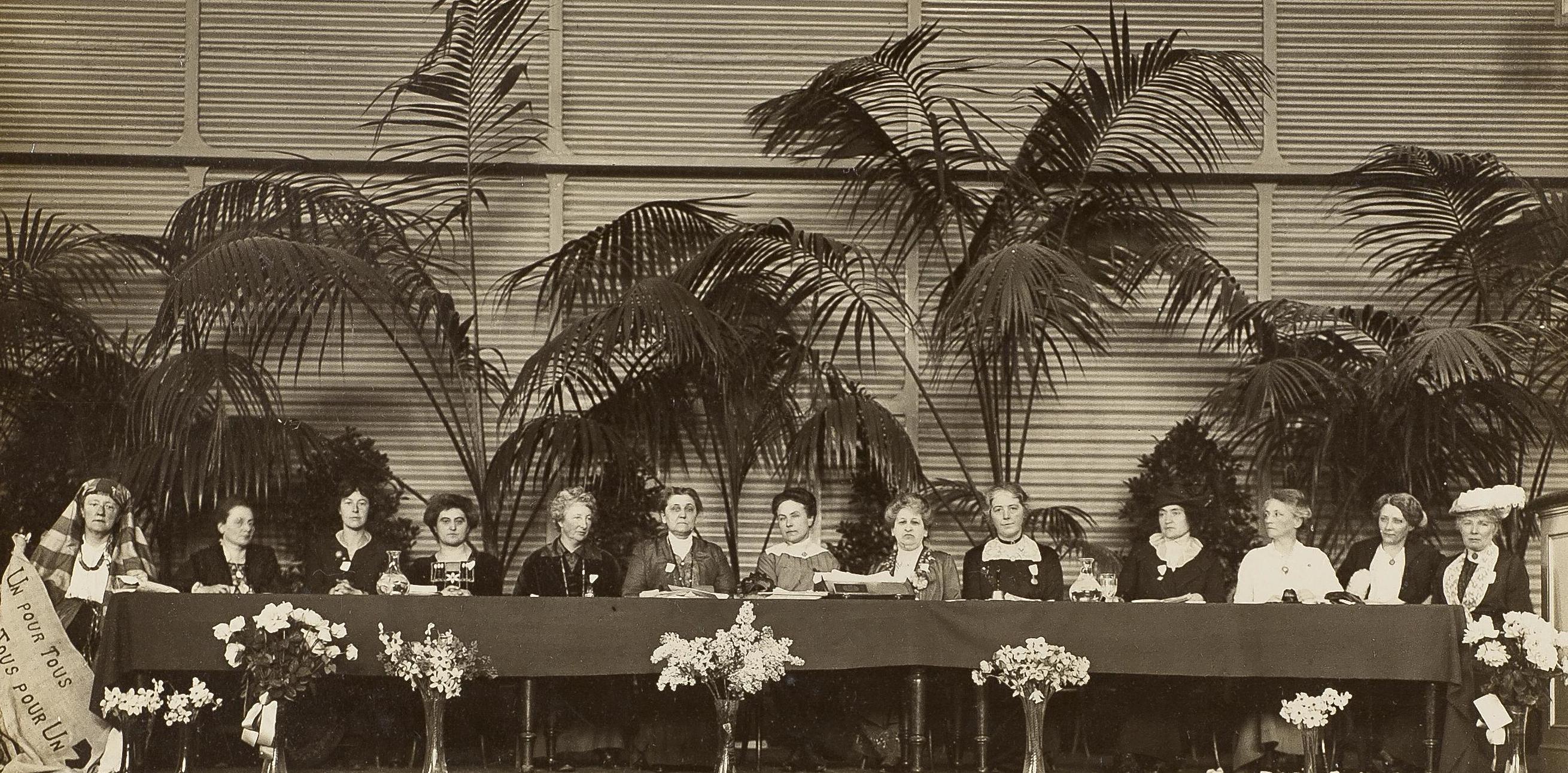

1938 - Campaign for a World Government
Rosika Schwimmer and Lola Maverick Lloyd were pioneering advocates for world federalism and women's rights, breaking barriers in the early 20th century.
In 1938 they founded the campaign for a World Government. Their radical vision for world peace led to several world-federalist movements and organizations.
They left behind a legacy as international peacebuilders and women's rights activists.

1945 - The United Nations
The United Nations is founded after World War II, with a broader and more effective mandate than the League of Nations. It serves as a forum for member states to address global issues and conflicts.

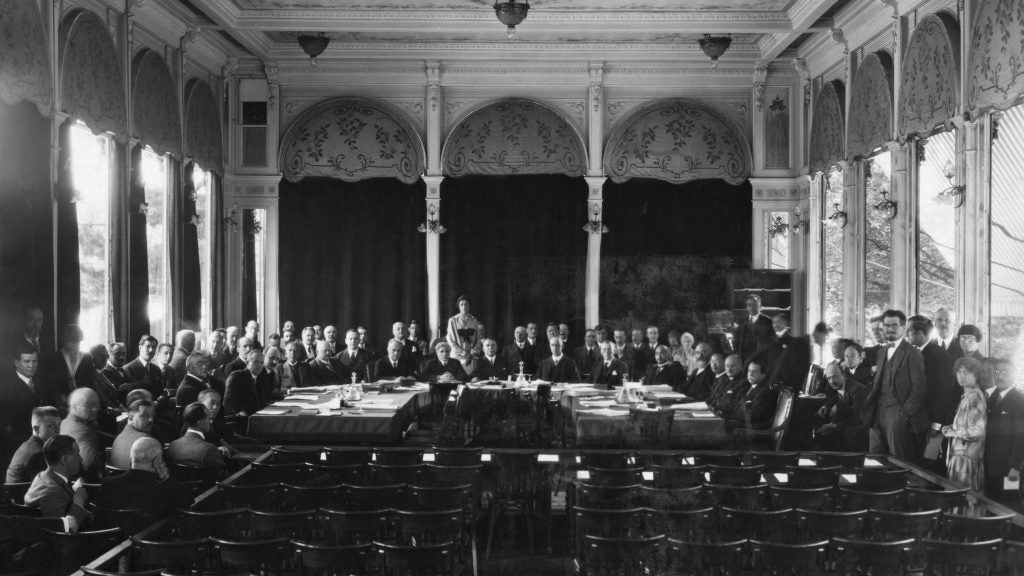
1947 - The World Federalist Movement
The World Federalist Movement is founded in Montreux, Switzerland, with the goal of promoting world federalism and the establishment of a global government.
1951 - The World Federalist Movement of Canada
In 1951, five independent world federalist groups in Montreal, Ottawa, Toronto, Winnipeg and Saskatoon came together to endorse a national constitution and form the World Federalists of Canada. Formal Government of Canada letters patent were obtained in 1965. A sister organization, a CRA registered charitable organization, the World Federalist Foundation was established in 1986.

1950s-60s - The Cold War
The Cold War and the ideological divide between the United States and the Soviet Union hinder significant progress towards world federalism. However, proponents continue to promote the idea through various organizations and initiatives.
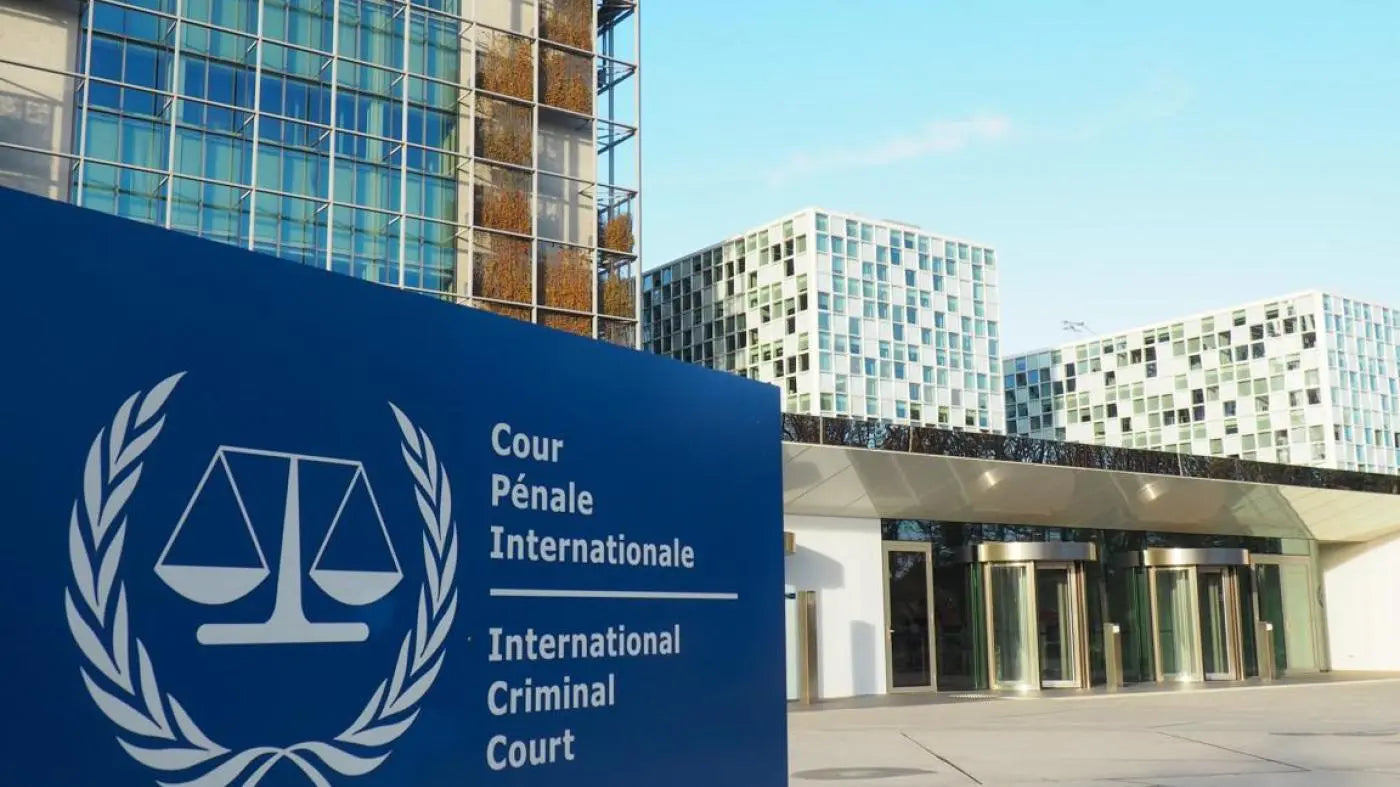

1999 - Establishment of the International Criminal Court
Amidst the shifting geopolitical landscape following the end of the Cold War, a resurgence of interest in international cooperation and global governance emerged. At the forefront of this movement stands the establishment of the International Criminal Court (ICC), hailed as a pivotal stride towards fortifying the framework of international law.
Founded on the principle of universal jurisdiction, the ICC embodies a collective commitment to hold individuals accountable for the most egregious crimes that transcend national boundaries. Its inception marks a decisive move towards fostering a robust and impartial system of international justice, reflecting the global community's dedication to upholding human rights and preventing impunity on a worldwide scale.
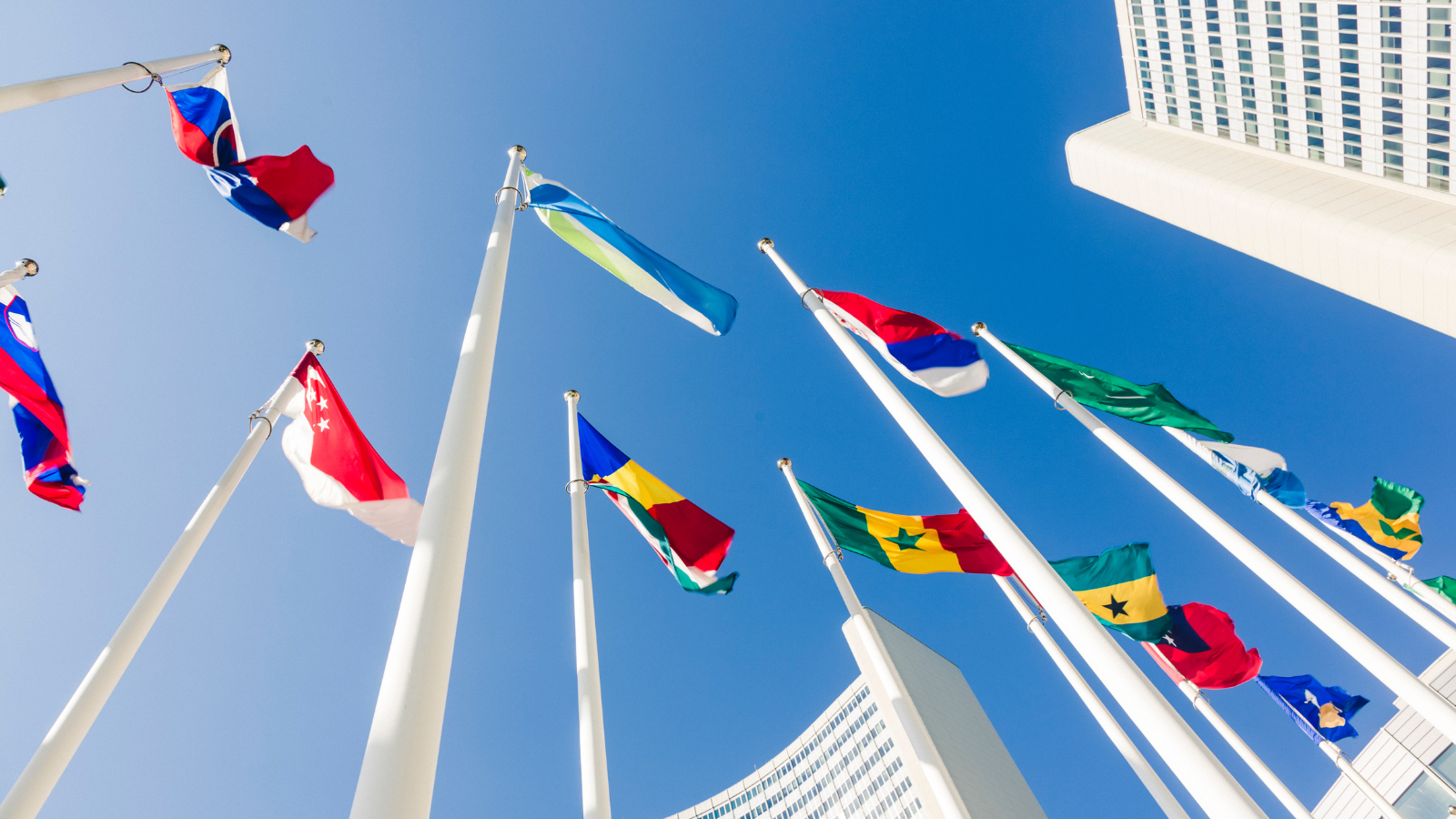

2000 - Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Summit adopts the United Nations Millennium Declaration, outlining goals for international development and cooperation in the 21st century, known as the Millennium Development Goals.

2000s-2010s Climate Awareness
The world sees increasing challenges such as climate change, global terrorism, and economic inequality, which spur discussions about the need for stronger global governance mechanisms.

2010: WFM-C advocacy for R2P
2010: The WFM-C continues its advocacy for the Responsibility to Protect (R2P) principle, emphasizing the international community's duty to prevent mass atrocities and protect civilians.

2020s - COVID-19 Global Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic highlights the interconnectedness of the world and the need for coordinated global responses to health crises and other global challenges.
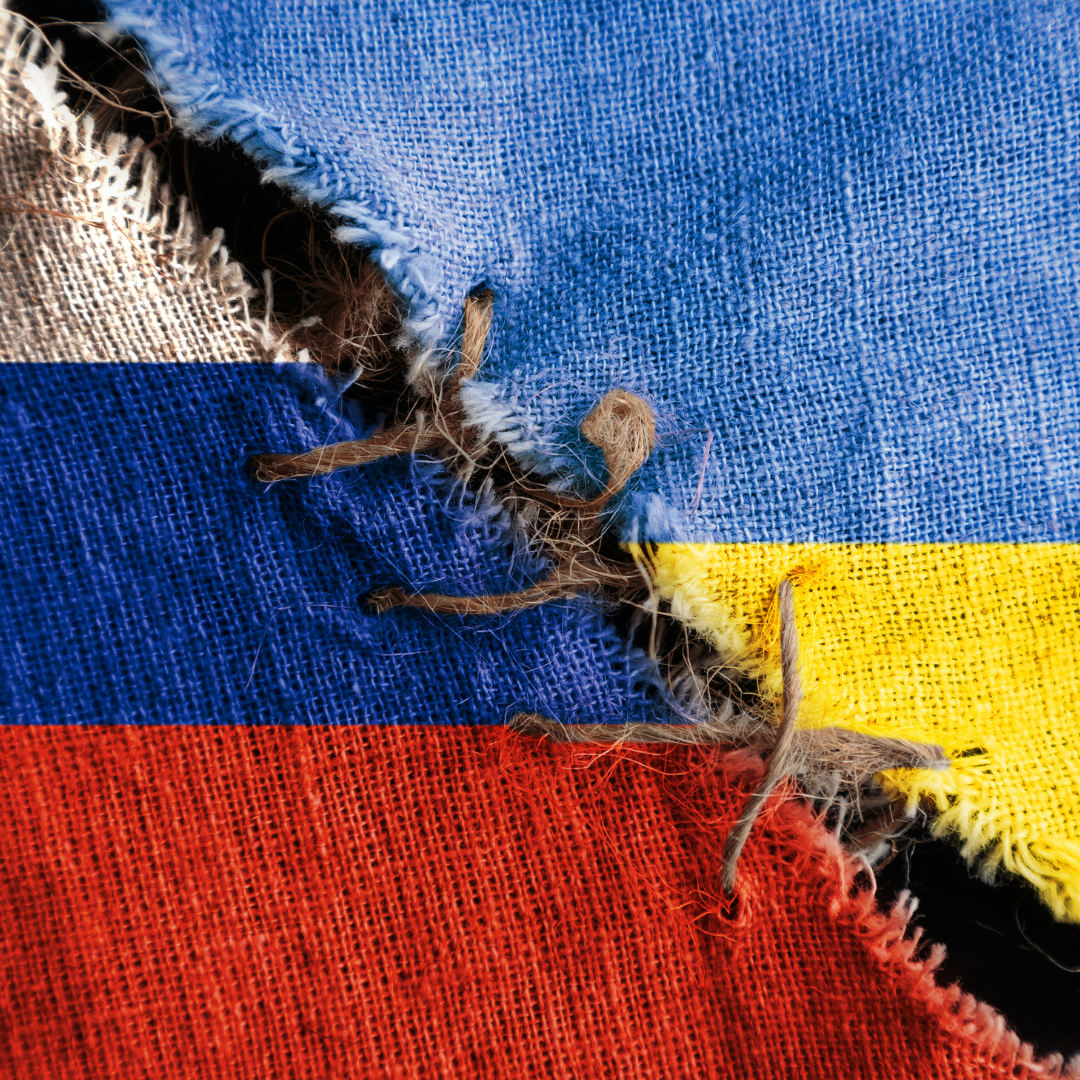

2022 - Russia's Illegal invasion of Ukraine
War in Ukraine sparks international dialogues on the efficacy of international institutions to confront modern problems. The conflict sheds light on the limitations of UN institutions, particularly the Security Council, in effectively addressing and preventing such conflicts.
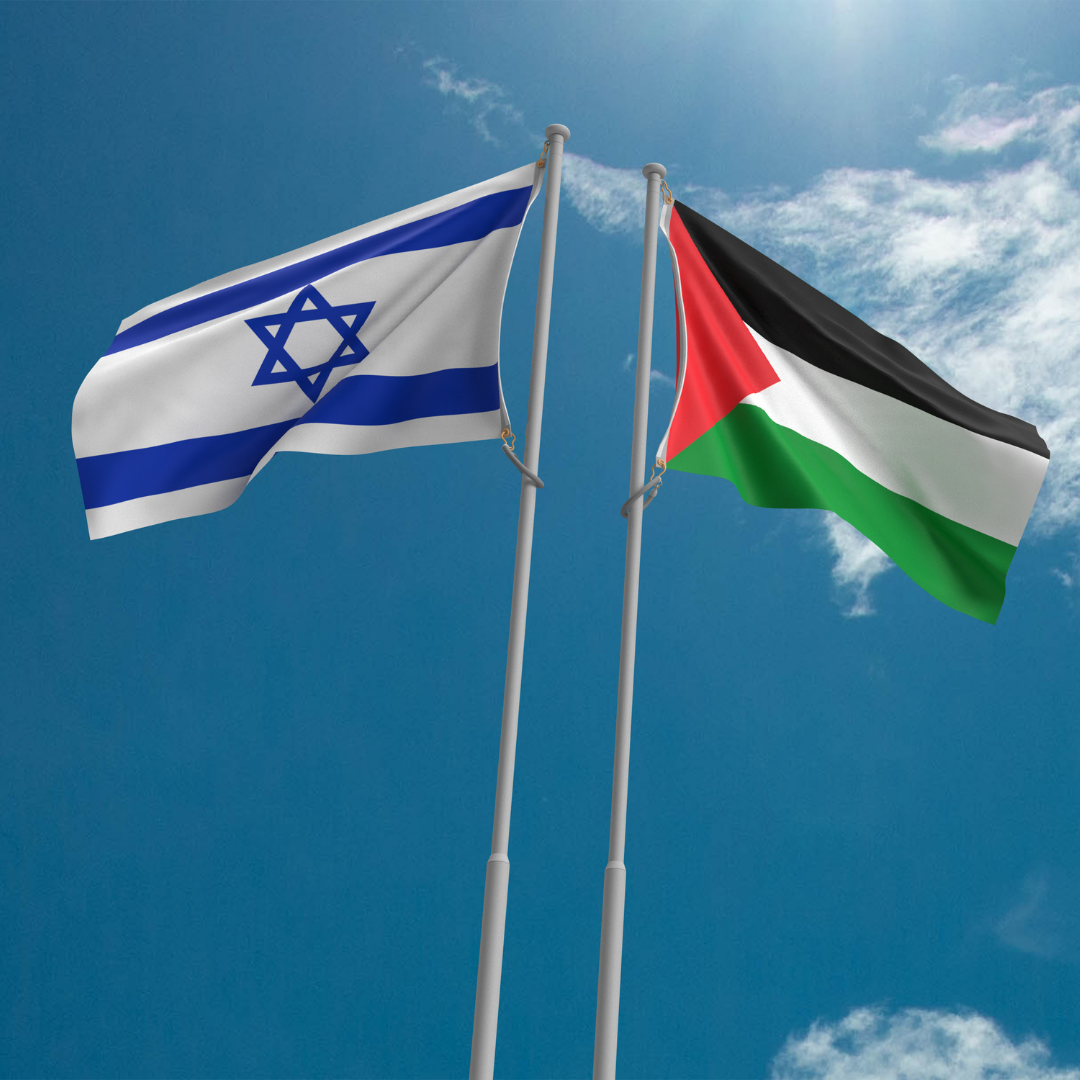

2024 - U.N. General Assembly Adopts Resolution in Support of Palestinian Statehood
The United Nations General Assembly approved the resolution by a vote of 143 to 9 with 25 nations abstaining, a highly symbolic move that reflects growing global solidarity with Palestinians. It also highlights the rebuke of Israeli militarism and the United States repeated use of the veto to block ceasefire resolutions at the Security Council and block full membership for a Palestinian State in the UN.
